What is a CNC machine tool?
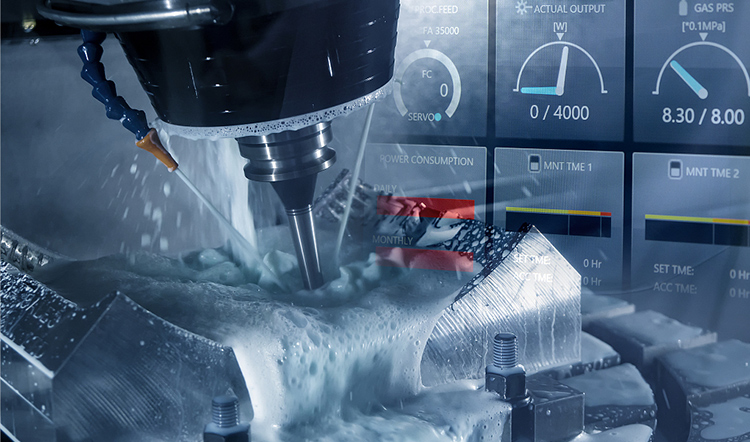
A CNC machine tool is a machine tool that can be controlled by a computer program. It can automatically complete various complex processing tasks according to preset processing programs. CNC is the abbreviation of “Computer Numerical Control”, which is computer numerical control.
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled machine tools to remove workpiece material to produce parts. Normally, CNC machine tools automatically plan the processing path based on the three-dimensional CAD model and control the tool to cut along the path to achieve the shape of the part.
This article will introduce the different types of CNC machine tools and how they work.
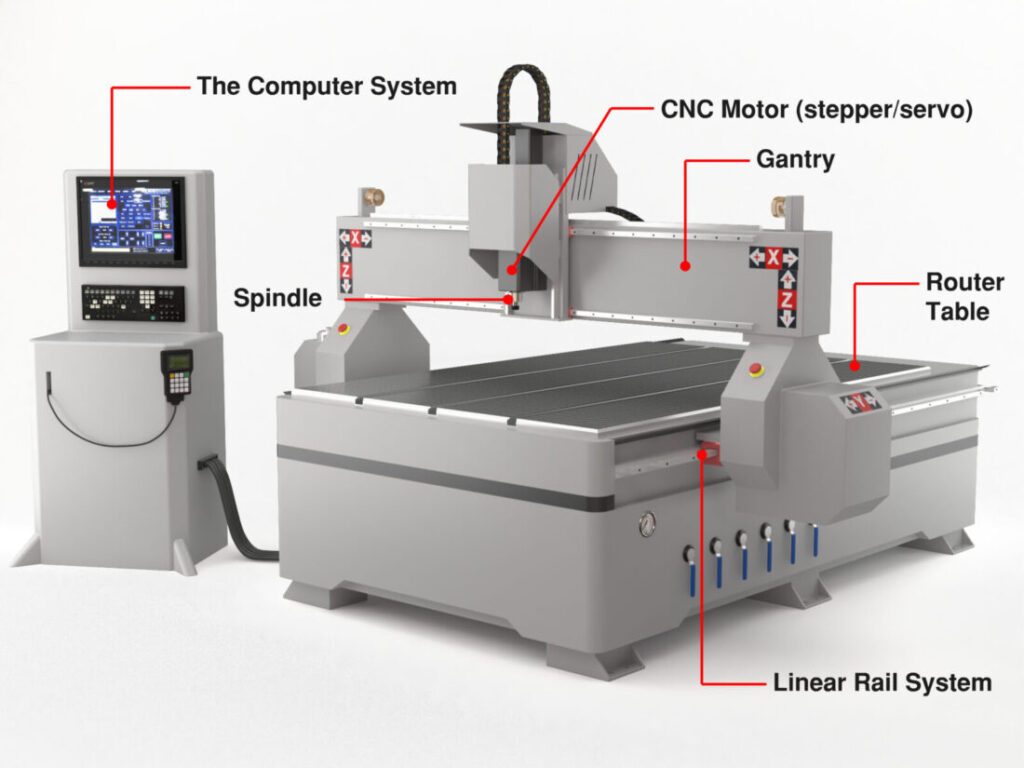
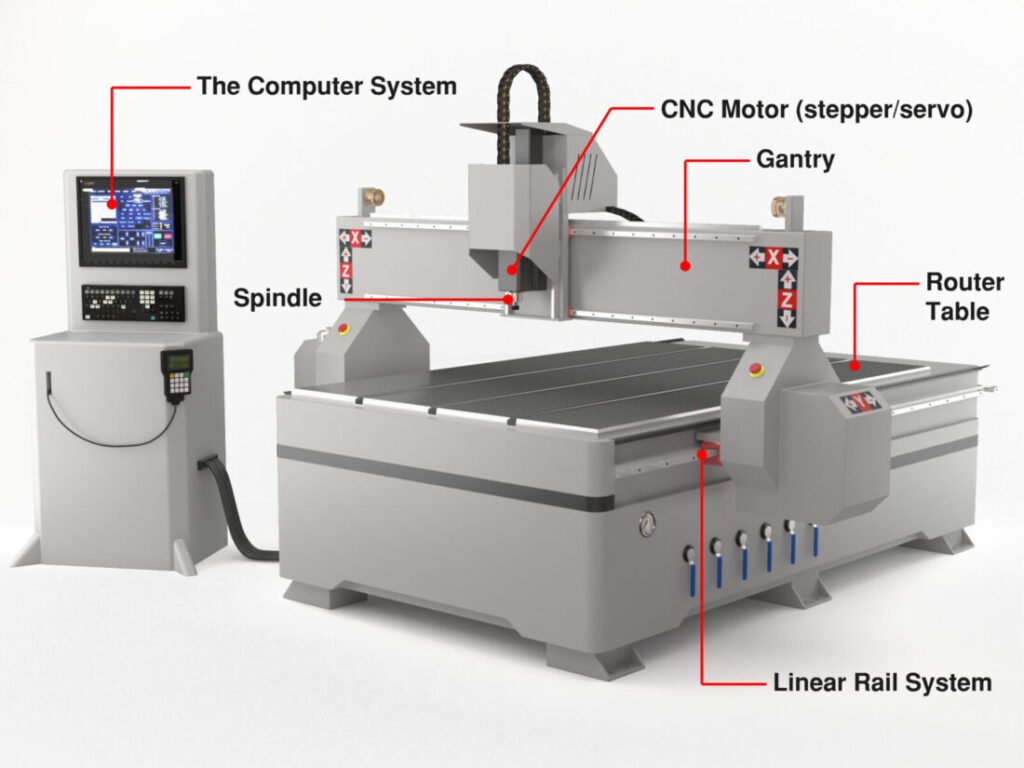
1.Router CNC Machine
A router CNC machine is like a CNC mill but is generally used for machining softer materials and is typically less precise than CNC Mills. CNC routers are known for their ability to use computer numerical control to route spindle and machine tool paths to design and shape materials like wood, steel, foam, composites, aluminum, and plastic.
CNC routers typically consist of stepper motors, stepper drivers, a mechanical base, a spindle, controllers, and a power supply. CNC routers help to reduce waste, increase productivity and accuracy, and produce products faster.
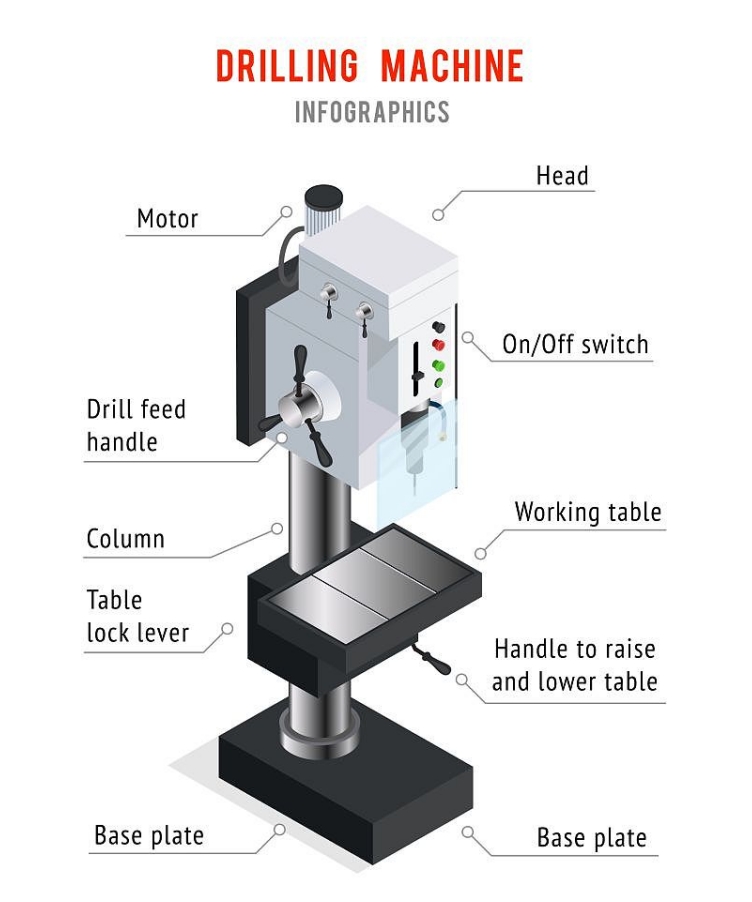
2. Drilling CNC Machine
A drilling CNC machine is used for machining processes that require producing cylindrical holes in a workpiece through drilling. It employs rotating drill bits whose design allows the waste metal, known as chips, to fall away from the workpiece during hole-making.
There are several common types of drill bits that can be used with a drilling CNC machine, each suited for different applications. Types include spotting drills for starting holes, peck drills for deep hole drilling, screw machine drills for precise holes, and chucking reamers for finishing holes to the desired size.
Like other CNC machines, a drilling CNC machine uses computer numerical control to automate the drilling process. It directs the drill bit locations and movement patterns according to programmed tool paths. This allows for precision drilling of multiple holes in a workpiece with accuracy and repeatability. Drilling CNC machines are useful when large volumes of parts need identical hole patterns or sizes produced through automated drilling processes.
3. Lathe CNC Machine
A Lathe CNC machine is used for machining processes that involve turning or shaping rotating workpieces. It employs single-point cutting tools whose design varies based on the particular turning application, such as roughing, finishing, facing, threading, forming, undercutting, parting and grooving.
The Lathe CNC machine automates the turning process through computer numerical control. It directs the cutting tool locations and movements according to programmed tool paths. This allows complex shapes and geometries to be produced from cylindrical workpieces with precision and repeatability.
There are different types of CNC lathes suited for various applications. Common types include turret lathes suitable for mass production with automatic tool changes, engine lathes for general purpose turning, and special-purpose lathes designed for specific geometries or materials.
The CNC turning process enhances productivity over manual lathes by enabling unmanned operation and production of multiple parts to exact specifications. Lathe CNC machines are especially useful in automotive, aerospace and precision manufacturing industries where a large number of turned components need to be machined accurately and efficiently.
4. 5-Axis CNC Machine
A 5-axis CNC machine enhances the capabilities of traditional 3-axis milling machines by adding two additional rotational axes, enabling machining of complex geometries in a single clamping.
In addition to the three linear axes (X, Y, Z) for positioning the cutting tool, a 5-axis CNC machine incorporates either two additional rotational axes at the cutting spindle or a tilting/rotating table. This provides two more degrees of freedom for positioning the workpiece.
By tilting and rotating the work holding fixture (trunnion table), the 5-axis machine allows the cutting tool to access and machine five faces of a prismatic workpiece at 90-degree angles without needing to reset the workpiece between operations.
The two additional rotary axes (typically called A-axis and C-axis) significantly improve machining efficiency by removing the need for multiple clamping and setups. Intricate geometries like sculpted forms can be machined complete in a single clamping on a 5-axis CNC machine.
It finds wide applications in the aerospace, die/mold and medical industries where complex parts are common. 5-axis CNC machining is also often utilized for sculpting due to its ability to machine freeform surfaces.
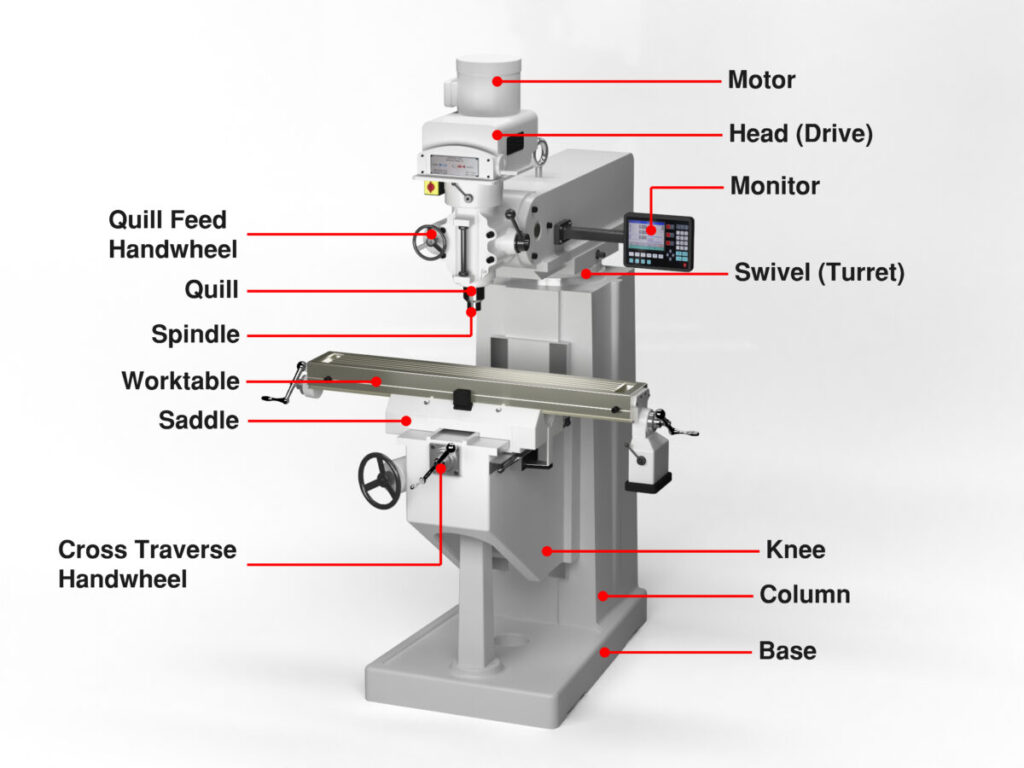
5. Milling CNC Machine
A Milling CNC machine utilizes rotating multi-point cutting tools to precisely shape and machine workpieces. Common milling tools include end mills, helical mills, and chamfer mills, which can be oriented either horizontally or vertically based on the specific milling application.
The Milling CNC machine automates the milling process through computer numerical control. It directs the cutting tool location and movement path according to programmed toolpaths. This enables complex profiles and geometries to be produced from raw materials or castings with precision and repeatability.
Milling CNC machines, also referred to as mill machines or mills, are available in both horizontal and vertical orientations. Basic CNC mills provide three linear axes of movement (X, Y, Z), while more advanced models incorporate additional rotary axes for increased accessibility.
Common types of CNC milling machines include hand mills for small parts, plain or vertical mills for general machining, universal mills suitable for a variety of operations, and omniversal mills offering maximum flexibility through four or five axes.
The CNC milling process enhances productivity over manual mills. It allows unmanned and mass production of milled components to tight tolerances. Milling CNC machines are widely used in manufacturing industries for machining parts from metals, plastics, wood, composites and more.
6. Laser Cutting CNC Machine
A laser cutting CNC machine utilizes a high-power laser to cut materials by melting, burning, or vaporizing them. It allows for precise cutting of intricate patterns and profiles.
The main types of industrial laser used in laser cutting machines include:
- CO2 lasers: One of the most common gas lasers using a carbon dioxide gas mixture. Suitable for cutting non-metals like wood, plastics, textiles. Can also cut some mild steels.
- Solid-state lasers: Typically Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (YAG) lasers using Neodymium as the active element. More powerful than CO2 lasers and capable of cutting thicker and harder metals.
- Fiber lasers: A newer solid-state laser type with superior beam quality. Very efficient for precision metal cutting applications.
Laser cutting CNC machines direct the laser beam according to programmed toolpaths using x-y gantries and CNC control. Common work sizes range from desktop to large format machines.
The laser provides a clean cut with high accuracy and minimal heat-affected zone. It allows intricate cutting of a wide range of materials. Laser cutting is widely used in manufacturing, prototyping and the automotive/aerospace industries.
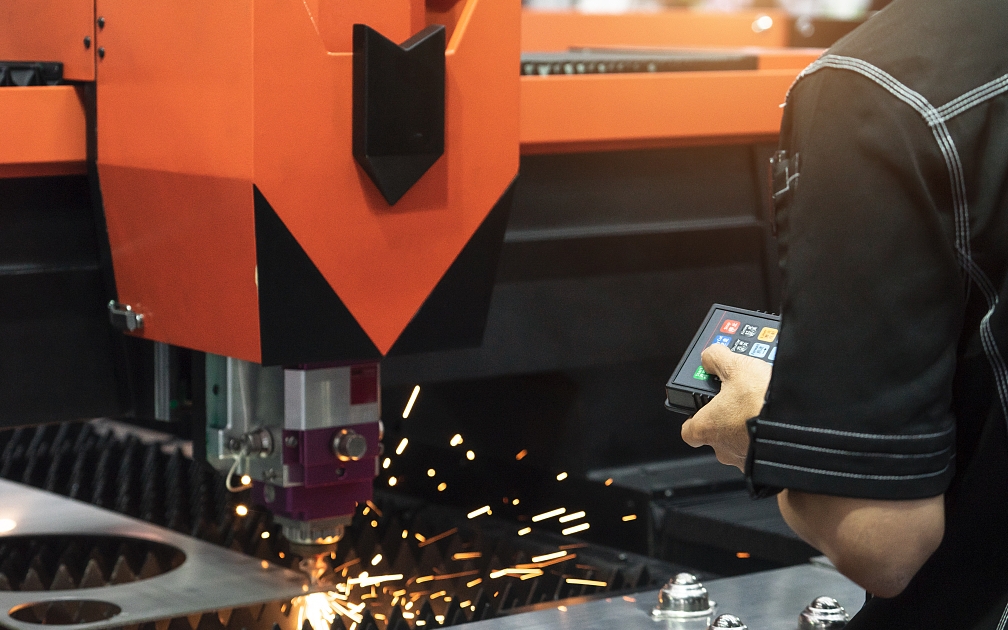
7. Plasma Cutting CNC Machine
A plasma cutting CNC machine utilizes a plasma torch to cut electrically conductive materials. It works by passing a high-velocity gas, such as oxygen or air, through a nozzle and forming an electric arc under the torch that ionizes the gas into a conductive plasma stream.
The plasma stream then transfers the heat and electricity onto the workpiece material, cutting through it by melting and vaporizing. Common materials cut on plasma cutting machines include steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass and copper.
On a CNC plasma cutting machine, the plasma torch is controlled by the CNC system according to programmed toolpaths. This allows for precise computer-controlled cutting of complex 2D and 3D shapes from metal.
Key features of plasma cutting CNC machines include the ability to cut thick plate materials, good cut quality with minimal heat-affected zones, and fast cutting speeds. They are well-suited for fabrication, maintenance and repair applications.
The CNC system provides automated, repeatable cuts and allows for unmanned operation. Plasma cutting is widely used in industries such as automotive, manufacturing, shipbuilding and construction for cutting, beveling and gouging of metal parts and components.
8. Electric Discharge CNC Machine
An electric discharge CNC machine, also known as an EDM (electric discharge machining) or spark erosion CNC machine, utilizes the thermoelectric process of electric sparks to cut electrically conductive materials.
It works by using electric sparks produced via a voltage difference between two electrodes – a tool electrode and the workpiece material – to wear away tiny amounts of material through melting and vaporization. Deionized water is used to flush away debris.
On an EDM CNC machine, the tool electrode is connected to the CNC system and precisely positioned and controlled according to programmed toolpaths. This allows for complex 3D shapes to be machined from hard metals and alloys that are difficult to cut with traditional methods.
Some key advantages of EDM CNC machines include the ability to machine very hard materials, produce parts with very high accuracy and surface finishes, and cut complex internal cavities and profiles.
Common applications include molds, dies, aerospace components and surgical implants due to the process being non-contact and generating minimal mechanical forces on the workpiece. EDM CNC machines are well-suited for low-volume production of complex parts.
9.Here are the key points about a Grinding CNC Machine:
- - A grinding CNC machine uses a rotating abrasive wheel to cut and shape metal parts through the mechanical process of abrasion.
- - The abrasive grinding wheel, usually made of diamonds or CBN (cubic boron nitride), removes small chips of metal when brought into contact with the workpiece. Precise control is needed to achieve tight tolerances.
- - On a CNC grinding machine, the grinding wheel and workpiece are precisely positioned and moved by the CNC system according to a programmed code. This enables complex 3D profiles to be ground automatically.
- - Common grinding operations include cylindrical grinding (external or internal surfaces), surface grinding (flat surfaces), centerless grinding and profile grinding.
- - Parts made with grinding CNC machines require very high accuracy and surface finishes. They are often precision mechanical components like camshafts, ball bearings, gears.
- - Industries that utilize CNC grinding include automotive, aerospace, medical and general manufacturing where tight tolerances are critical.
- - Advantages over conventional grinding include repeatable accuracy, multi-axis control and the ability to grind complex contours and profiles unattended.
So in summary, a grinding CNC machine precisely shapes metal parts through automated abrasive wheel machining controlled by a computer numerical control system.
10. Here are the key points about a CNC Machine with Automatic Tool Changes:
- - It has a tool magazine/carousel that holds multiple tools such as drills, mills, routers etc. adjacent to the machine workspace.
- - The automatic tool changer allows quick and automatic replacement of tools as needed during the CNC machining process without manual intervention.
- - This significantly improves productivity by minimizing non-cutting time compared to manual tool changes. Complex parts requiring multiple tools can be machined without stopping the process.
- - Tools are picked up/exchanged robotically from the magazine and mounted onto the spindle using an automatic tool changing arm under CNC control.
- - It increases the tool carrying capacity of the machine beyond a single tool, allowing machining of more complex parts without reloading tools manually.
- - Broken or worn tools can be replaced on the fly without stopping the whole production. This improves reliability and uptime.
- - Automatic tool calibration may also be possible to ensure geometric accuracy after each change.
- - It moves CNC machining towards more efficient lights-out/unmanned production with minimal human intervention.
So in summary, automatic tool changing improves flexibility and productivity of CNC machines.
Post time: Dec-08-2023